TheHive
TheHive is an open-source security incident response platform designed to help organisations efficiently manage and respond to cybersecurity incidents. Developed to facilitate collaboration among security teams, it provides a centralised system for tracking and investigating security events, alerts, and cases.
Lab Setup for Proof of Concept
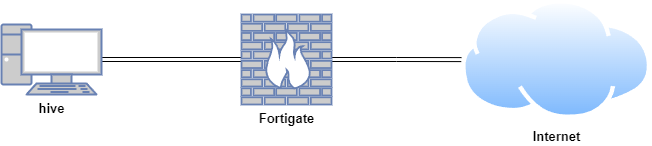
In this proof of concept, TheHive was installed on an Ubuntu Virtual Machine (VM).
| Host | OS | Role | IP Address |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fortigate | Fortios 7.6.0 | Firewall/Router | 192.168.1.111 (WAN) / 10.0.0.1 (LAN) |
| hive | Ubuntu 22.04 LTS | TheHive VM | 10.0.0.40 |
Install TheHive Offline
Download the dependencies
On an internet-connected Ubuntu machine, make a folder called the hive-package
Download openjdk 11
#wget http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/o/openjdk-lts/openjdk-11-jdk_11.0.24+8-1ubuntu3~22.04_amd64.deb
Add the Cassandra, StrangeBee and Elasticsearch repositories and its GPG keys:
wget -qO - https://downloads.apache.org/cassandra/KEYS | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/cassandra-archive.gpg
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/cassandra-archive.gpg] https://debian.cassandra.apache.org 40x main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cassandra.sources.list
wget -O- https://archives.strangebee.com/keys/strangebee.gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/strangebee-archive-keyring.gpg
echo 'deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/strangebee-archive-keyring.gpg] https://deb.strangebee.com thehive-5.2 main' | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/strangebee.list
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/elasticsearch-keyring.gpg
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/elasticsearch-keyring.gpg] https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/8.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-8.x.list
Update and download the required packages without installing:
This will download all packages into the cache /var/cache/apt/archives/
sudo apt update
sudo apt-get install -y --download-only cassandra
sudo apt-get install -y --download-only thehive
sudo apt-get install -y --download-only elasticsearch
Run the following command to copy the required files and dependencies to the hive-package
cd /var/cache/apt/archives
cp openjdk-11-jre-headless_11.0.24+8-1ubuntu3~22.04_amd64.deb cassandra_4.0.13_all.deb java-common_0.72build2_all.deb ca-certificates-java_20190909ubuntu1.2_all.deb thehive_5.2.14-1_all.deb elasticsearch_8.15.1_amd64.deb ~/hive-package/
Compress the hive-package directory
Transfer and extract the hive-package on the air-gapped machine
Install the deb packages
Configure TheHive
Edit /etc/cassandra/cassandra.yaml
Leave cluster names as ‘Test Cluster’
Change the listen_address, rpc_address and the seeds to your IP address
cluster_name: 'Test Cluster'
...
listen_address: 10.0.0.40
...
rpc_address: 10.0.0.40
...
seed_provider:
# Addresses of hosts that are deemed contact points.
# Cassandra nodes use this list of hosts to find each other and learn
# the topology of the ring. You must change this if you are running
# multiple nodes!
- class_name: org.apache.cassandra.locator.SimpleSeedProvider
parameters:
# seeds is actually a comma-delimited list of addresses.
# Ex: "<ip1>,<ip2>,<ip3>"
- seeds: "10.0.0.40:7000"
Stop cassandra, remove the system keyspace data and then start cassandra. \
Verify that cassandra service is active and running.
systemctl stop cassandra
rm -rf /var/lib/cassandra/data/system/*
systemctl start cassandra.service
systemctl status cassandra.service
Edit /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
Uncomment the cluster name and change it to thehive
Uncomment the node name and leave it as node-1
Uncomment the network host and change it to your IP address
Uncomment the http port: 92000
Uncomment the cluster initial master nodes and remove node-2
Comment the cluster initial master nodes “hive”
cluster.name: thehive
...
node.name: node-1
...
network.host: 10.0.0.40
...
http.port: 9200
...
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
...
# Enable security features
xpack.security.enabled: false
xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: false
...
#cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["hive"]
Start and enable elasticsearch. Verify elasticsearch service is active and running.
Change the ownership of the /opt/thp directory to thehive user and group.
Verify the ownership
chown -R thehive:thehive /opt/thp
ls -la /opt/thp
total 12
drwxr-xr-x 3 thehive thehive 4096 Sep 7 17:12 .
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Sep 7 17:12 ..
drwxr-xr-x 5 thehive thehive 4096 Sep 7 17:12 thehive
Edit /etc/thehive/application.conf
Change the host name and application baseURL to your IP address
Make sure cluster-name matches with the cluster name defined in cassandra.yaml
To ensure TheHive is listening on the correct IP address and port, add the following lines under the service configuration:
db.janusgraph {
storage {
backend = cql
hostname = ["10.0.0.40"]
# Cassandra authentication (if configured)
# username = "thehive"
# password = "password"
cql {
cluster-name = "Test Cluster"
keyspace = thehive
}
}
index.search {
backend = elasticsearch
hostname = ["10.0.0.40"]
index-name = thehive
}
}
...
# Service configuration
application.baseUrl = "http://10.0.0.40:9000"
play.http.context = "/"
play {
http {
address = "0.0.0.0" # Listen on all interfaces or set to "10.0.0.40" to bind to that IP
port = 9000
}
}
Start and enable thehive service. Verify it is active and running.
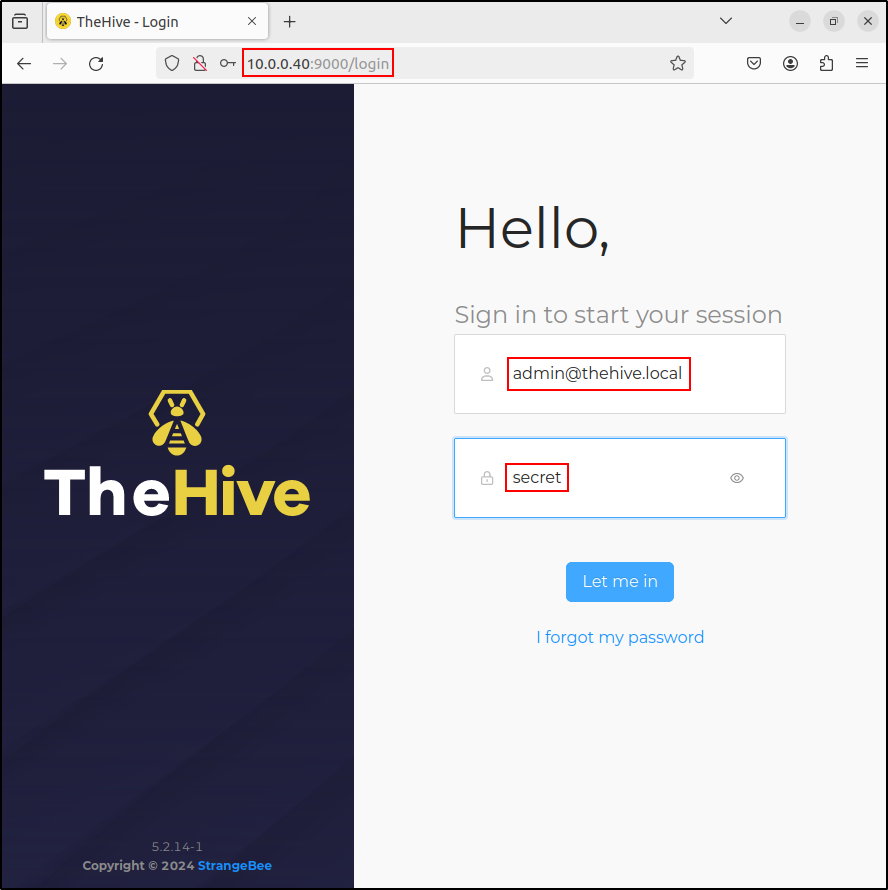
Navigate to thehive dashboard http://10.0.0.40:9000
Login using default credentials admin@hive.local (password: secret)
References
- https://github.com/MyDFIR/SOC-Automation-Project/blob/main/TheHive-Install-Instructions
- https://youtu.be/YxpUx0czgx4?si=-B57fRikVW8AVORo
- https://youtu.be/VuSKMPRXN1M?si=JctwPim-_c3ydR-E